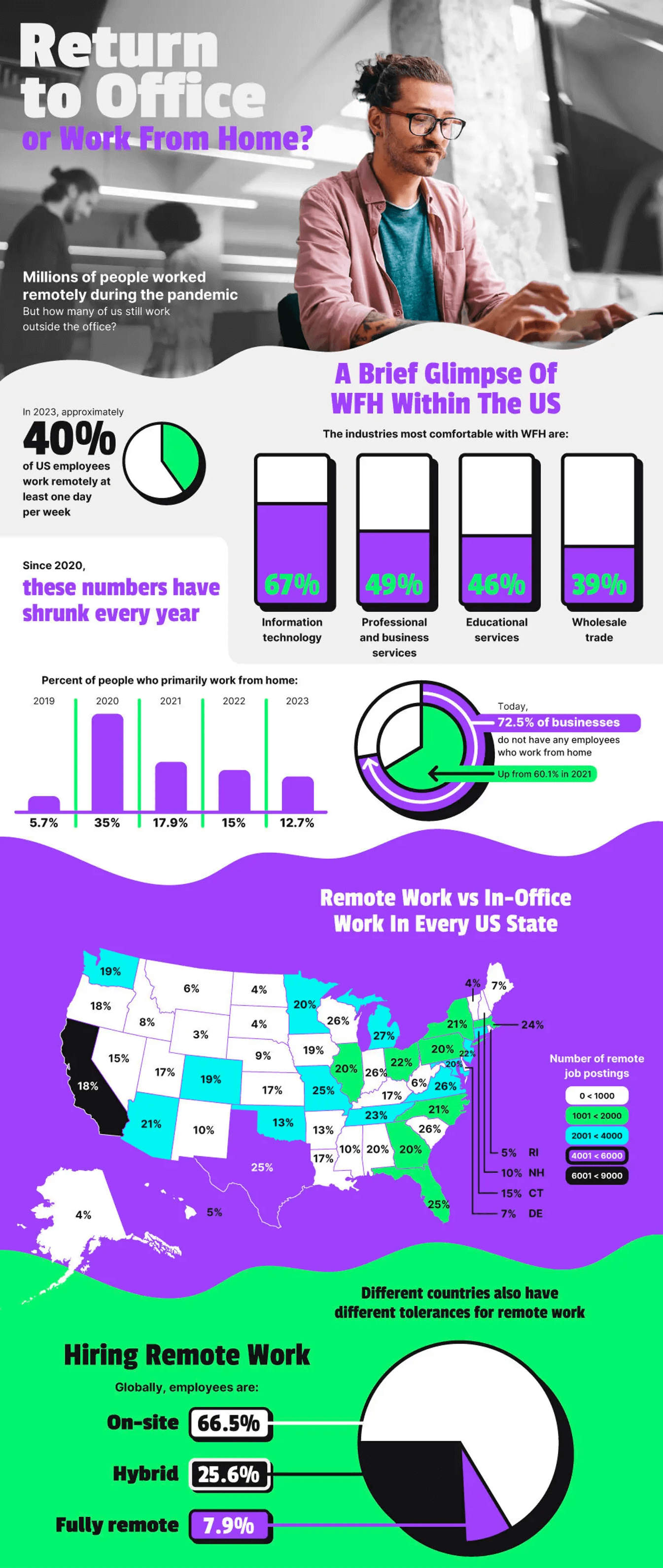
The pandemic initiated an irreversible shift in American work culture, leading to a new era of remote work. In 2023, 40% of U.S. employees worked remotely at least once weekly. The leading sectors in this transformation were Information Technology (67%), Professional and Business Services (49%), Educational Services (46%), and Wholesale Trade (39%). This trend, however, has seen a decline from its 2020 peak.
Comparatively, a majority of businesses (72.5%) reported having no remote employees in 2023, a significant increase from 2021’s 60.1%. State-wise, Michigan led with 27% of its workforce remote, while Wyoming had the least at 3%. On a global scale, the workforce primarily remains on-site (66.5%), with hybrid (25.6%) and fully remote models (7.9%) also present.
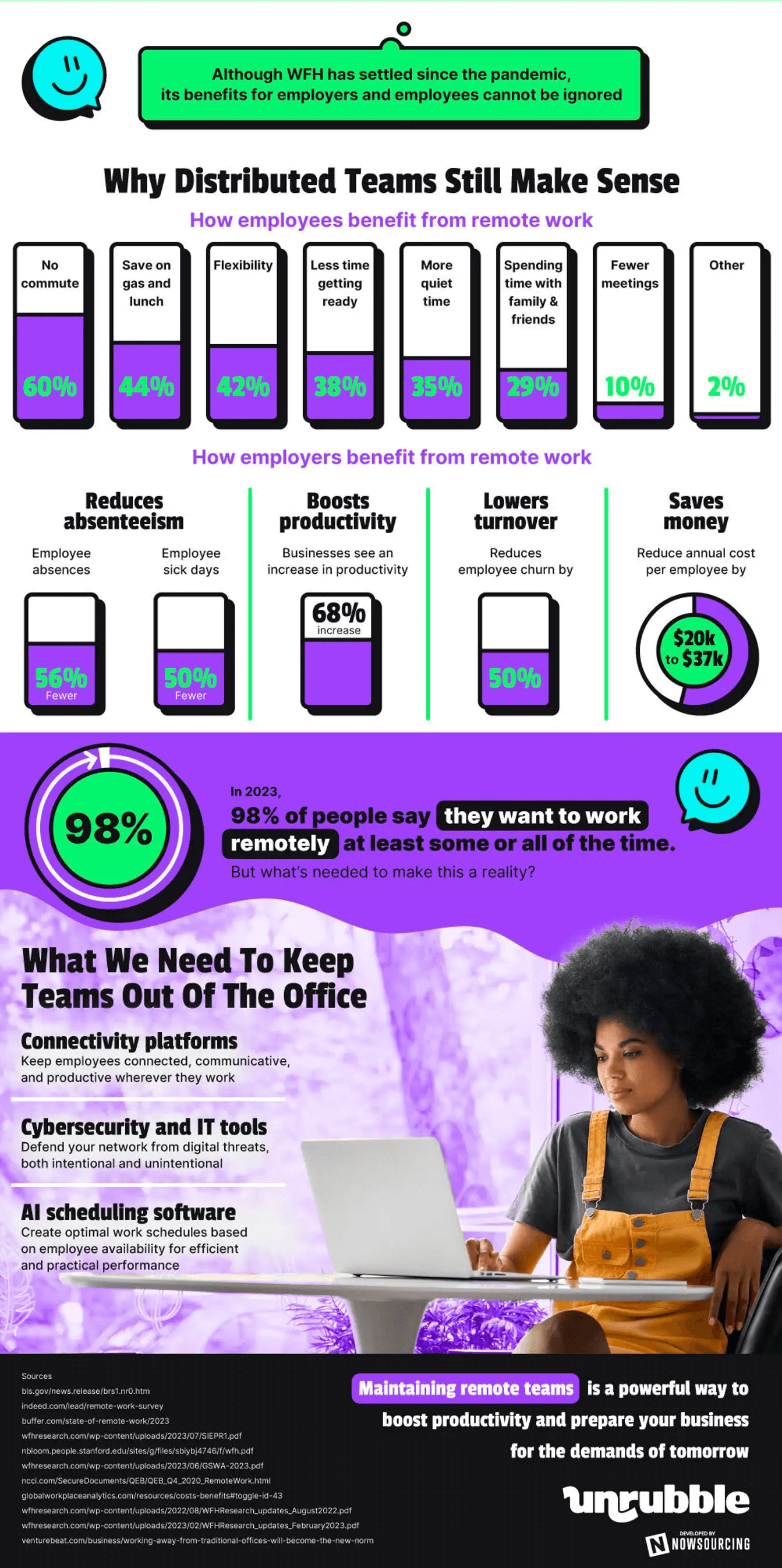
Remote work benefits both employees and employers. Employees enjoy no commute (60%), savings (44%), and flexibility (42%). Employers experience fewer absences (56% reduction) and sick days (50% reduction), along with a productivity boost (68%). Notably, 98% of individuals in 2023 preferred remote work in some form. To sustain this, businesses are investing in connectivity platforms, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence scheduling software, crucial for the future workforce landscape.
Infographic Source: https://unrubble.com/blog/remote-work-statistics
